Beyond Nvidia, Four Things to Know at Asia—this phrase encapsulates the transformative shifts occurring across Asia’s technology sectors in 2025. While Nvidia continues to be a significant player in AI and semiconductors, Asia’s broader tech ecosystem is experiencing rapid evolution driven by regional innovation, strategic investments, and geopolitical dynamics.
From China’s advancements in humanoid robotics to India’s burgeoning semiconductor initiatives and from South Korea’s leadership in memory chips to Japan’s ambitions in advanced chip manufacturing, Asia is redefining its role in the global tech arena. This article delves into four pivotal developments shaping Asia’s tech landscape beyond Nvidia’s influence.
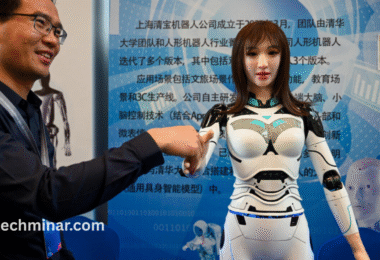
China’s Strategic Push in Humanoid Robotics
China is aggressively investing in AI-powered humanoid robots to revolutionize its manufacturing sector. Startups like AgiBot and MagicLab, backed by substantial government subsidies exceeding $20 billion, are deploying robots capable of complex tasks such as assembly and quality control. These initiatives aim to address challenges like an aging workforce and economic pressures. State procurement of humanoid robots has surged, with expenditures rising from 4.7 million yuan in 2023 to 214 million yuan in 2024.
The integration of advanced AI models like DeepSeek and Qwen enhances these robots’ capabilities, positioning China as a leader in embodied AI. Analysts predict that global sales of such robots could reach one million units by 2030, signaling a significant shift in manufacturing paradigms.
South Korea’s Leadership in Semiconductor Innovation
South Korea continues to solidify its position as a global semiconductor powerhouse. In 2022, the country accounted for 60.5% of the worldwide memory semiconductor market, with a DRAM market share of 70.5% and a NAND market share of 52.6%. Major companies like Samsung Electronics and SK Hynix are at the forefront, with SK Hynix leading the global DRAM market with a 36% share as of Q1 2025.
The government’s K-CHIPS Act, enacted in March 2023, provides tax credits of up to 25% for facility investments and up to 50% for R&D, fostering further growth. Additionally, plans are underway to construct the world’s largest semiconductor cluster in Gyeonggi Province, with an investment of approximately $470 billion over the next 23 years.
India’s Emergence in the Semiconductor Sector
India is making significant strides in establishing itself as a key player in the semiconductor industry. The Tata Group’s Semiconductor Assembly and Test facility in Jagiroad, Assam, represents a landmark project, with an investment of approximately INR 27,000 crore (around US$3.6 billion). Set to be operational by mid-2025, this facility is expected to produce 4.83 crore chips per day and generate over 25,000 direct and indirect jobs.
This initiative aligns with India’s broader Semiconductor Mission, aiming to reduce dependency on imports and bolster domestic production. Collaborations with global companies, such as a strategic deal between Tata Electronics and Tesla, further underscore India’s growing significance in the worldwide semiconductor supply chain.
Japan’s Ambitions in Advanced Chip Manufacturing
Japan is reasserting its role in the global semiconductor landscape through strategic investments and collaborations. The establishment of Rapidus Corporation in 2022, supported by major Japanese companies like Sony, Toyota, and SoftBank, aims to develop advanced semiconductor manufacturing capabilities, targeting a 2nm process by 2027.
This initiative is part of Japan’s broader efforts to become integral to the global supply chain for next-generation chips. The government’s substantial investments in R&D and subsidies for domestic and foreign companies are pivotal in achieving these objectives.
Southeast Asia’s Growing Role in Semiconductor Production
Southeast Asian countries are increasingly contributing to the global semiconductor industry. Malaysia, for instance, is the world’s sixth-largest exporter of semiconductors, accounting for 13% of global exports, primarily in less advanced chips. Thailand has announced a $345 million project to build its first front-end fab, expected to be operational by 2027.
Singapore is also enhancing its semiconductor manufacturing capabilities, with investments like the $10.5 billion wafer chip plant by NXP Semiconductors and Vanguard International Semiconductor Corporation. These developments underscore Southeast Asia’s growing importance in the global semiconductor supply chain.
Geopolitical Dynamics Influencing Asia’s Tech Landscape
Geopolitical tensions, particularly between the United States and China, are significantly impacting Asia’s technology sectors. Trade restrictions, tariffs, and territorial disputes are leading to supply chain disruptions and prompting countries to seek greater self-reliance in critical technologies.
In response, Asian nations are increasing investments in domestic semiconductor production, diversifying supply chains, and forming strategic alliances to mitigate risks associated with geopolitical uncertainties.
The Rise of AI Startups and Venture Capital in Asia
Asia is witnessing a surge in AI startups, supported by significant venture capital investments. For example, Bat VC, a New York-based venture capital firm founded by Indian tech veterans, has launched a $100 million fund to support early-stage startups in AI, fintech, and enterprise sectors across the US and India.
This trend reflects the growing global interest in Indian startups amid US-China trade tensions, with India becoming a key hub for tech innovation. The country’s strong IT ecosystem and focus on AI-driven solutions are attracting increased attention from investors and major tech companies.
Nvidia’s Strategic Expansion Beyond Big Tech
While Nvidia remains a dominant player in AI and semiconductors, the company is strategically expanding its customer base beyond significant tech firms like Amazon, Microsoft, and Google. Nvidia is targeting sovereign AI projects and emerging cloud providers, forming partnerships with nations and smaller companies to reduce reliance on hyperscalers.
Recent collaborations include a multibillion-dollar chip deal with Saudi Arabia’s Humain and partnerships with enterprise IT suppliers like Cisco, Dell, and HP. These moves aim to diversify Nvidia’s revenue streams and capture new markets in the evolving AI landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is driving China’s investment in humanoid robotics?
China aims to address labor shortages and enhance manufacturing efficiency by investing in AI-powered humanoid robots, which will be supported by substantial government subsidies.
How is South Korea maintaining its semiconductor industry leadership?
Through significant investments in R&D, tax incentives under the K-CHIPS Act, and plans to build the world’s largest semiconductor cluster, South Korea continues to lead in memory chip production.
What are India’s goals in the semiconductor sector?
India seeks to reduce import dependency and become a global semiconductor hub, with initiatives like the Tata Semiconductor Assembly and Test facility and strategic partnerships with international companies.
How is Japan contributing to advanced chip manufacturing?
Japan’s Rapidus Corporation, backed by major domestic companies, is working towards developing 2nm process technology by 2027, aiming to strengthen Japan’s position in the global semiconductor supply chain.
What role does Southeast Asia play in the semiconductor industry?
Countries like Malaysia, Thailand, and Singapore are expanding their semiconductor manufacturing capabilities, contributing significantly to the global supply chain.
How are geopolitical tensions affecting Asia’s tech industries?
Geopolitical tensions are prompting Asian countries to invest in domestic production, diversify supply chains, and form strategic alliances to mitigate risks.
What is the significance of AI startups in Asia?
The rise of AI startups, supported by venture capital investments, reflects Asia’s growing role in tech innovation, particularly in countries like India.
How is Nvidia expanding its market reach in Asia?
Nvidia is forming partnerships with emerging cloud providers and sovereign AI projects to diversify its customer base beyond significant tech firms.
Conclusion
Asia’s technology landscape in 2025 is marked by dynamic growth and strategic initiatives across various sectors. From advancements in robotics and semiconductors to the rise of AI startups and geopolitical adaptations, the region is redefining its role in the global tech arena, extending beyond the influence of major players like Nvidia.